The Data Governancealso known as Data Governancehas become an essential component for those organizations that wish to advance in their digital transformation and improve their competitiveness. In a world where data has become a critical asset, the need to establish clear policies, processes and roles for data management is becoming increasingly important.
But what does data governance really mean and how can a company implement it effectively without unnecessary complications? This article will guide you through everything you need to know: from the basics to the most sophisticated strategies implemented by market-leading companies.
Data Governance: practical and current definition
The Data Governance is a set of policies, standards, practices and roles that ensure that an organization's data is accurate, consistent, available and secure throughout its lifecycle. It is a management framework that ensures the quality, integrity, traceability and security of information.
As opposed to simple data management, the Data Governance establishes a clear decision structure on who can do what with the data, when and under what conditions. Its purpose is to ensure that data is a reliable resource for making strategic decisions.
The term Data Governance has gained popularity in international environments, while in Spanish it is more common to talk about Data Governance o Data Governance. Although different in nomenclature, they share the same principles.
To gain a clearer understanding of the components that make up a sound strategy of Data GovernanceThe following is a visual model with the 9 fundamental pillars of Data GovernanceThe data quality, data security, documentation and architecture are covered:
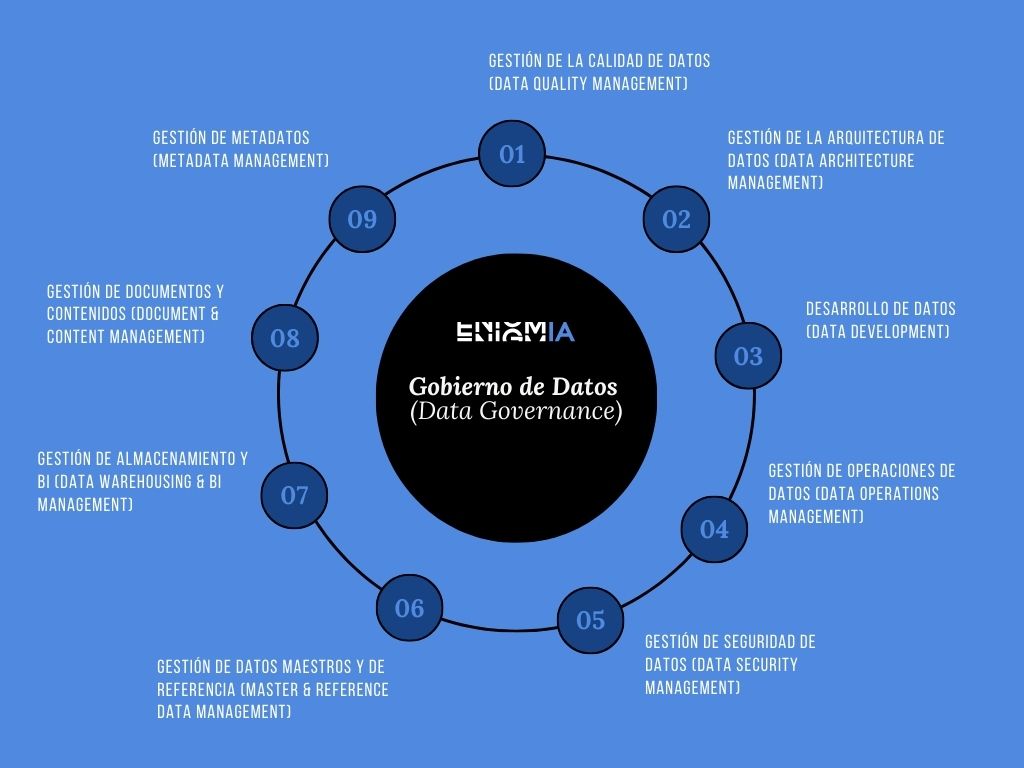
Each of these pillars represents a critical dimension within the data lifecycle and must be integrated in a coordinated manner in any governance initiative to be effective, sustainable and scalable.
Keys to Data Governance
Implement a solid strategy for Data Governance brings significant advantages to all types of organizations, from SMEs to multinationals.
Improve data quality:
By applying defined validation processes and standards, data inconsistencies, duplications and errors are eliminated. This is vital to avoid bad decisions and ensure accurate analysis.
2. Ensures regulatory compliance:
With regulations such as the RGPD o HIPAAIn order to meet these requirements, companies must demonstrate control over their data. A good governance system enables these requirements to be met in a structured way.
3. Risk reduction:
A clear policy on data use and access reduces the risks of leaks, unauthorized access and other security problems.
4. Strategic alignment:
Data Governance enables data to be available, accessible and aligned with business objectives, facilitating informed strategic decisions.
5. Resource optimization:
By standardizing processes, redundancy is avoided and efforts related to information management are optimized.
Pillars of Data Governance
A successful strategy of Data Governance is based on fundamental pillars that must be adapted to the context of each organization:
Policies and Standards:
It is necessary to define clear rules on how data should be managed. This includes privacy, security, quality, and retention policies.
Roles and Responsibilities:
Data Governance involves the participation of different profiles, such as the Chief Data Officer (CDO), Data Steward, Data Owner y Data Custodianeach with specific functions.
3. Architecture and Technology:
Having technological tools that facilitate cataloging, traceability, access control and process automation is essential to maintain effective governance.
4. Organizational culture:
The transformation to a data-driven culture requires that the entire organization understands the importance of data as a strategic asset.
5. Metrics and monitoring:
You cannot improve what you do not measure. Establishing KPIs (such as data quality, usage, compliance, etc.) is key to evaluate the impact of the strategy.
How to implement a Data Governance strategy
In order to effectively implement a Data GovernanceIn order to achieve this, it is necessary to follow a clear roadmap:
1. Initial assessment of data status:
Knowing the starting point is crucial for prioritization. A diagnosis of data maturity and current processes is recommended.
2. Definition of strategic objectives:
Every implementation must respond to a business need: To improve data quality, to comply with regulations, to optimize processes?
3. Design of the governance architecture:
Establish what roles will be responsible, what tools will be used, how access to data will be controlled, and how processes will be documented.
4. Training and communication:
Everyone involved must understand the new rules of the game. Training teams and spreading the data culture is essential to achieve organizational change.
5. Implementation, follow-up and continuous improvement:
Governance is not a project with an end, but an ongoing process that must adapt to business growth and new regulations.
Real-world use cases
The principles of Data Governance are applied in a practical way in the different sectors we work with, adapting to their specific needs, regulations and operating context. Here are some concrete examples:
- Insurance: implement Data Governance policies to validate customer information, reduce fraud and optimize risk management with accurate data.
- Public Sector: implements strategies for Data Governance to ensure transparency, traceability and control of citizen data, complying with regulations such as the National Security Scheme or laws on access to public information.
- Retail y Mass Consumption: manage large volumes of customer, product and logistics data. Data Governance helps to unify sources, improve customer experience and personalize campaigns.
- Education: universities and training centers apply governance to maintain academic records, performance statistics and administrative data with quality, privacy and security criteria.
- Media and Communications: use Data Governance to manage multimedia content, metadata, usage rights and audience analysis in a structured and secure way.
- Private Equity and Financial Sector: need robust governance models to ensure the quality and security of data in investment, audit and financial reporting processes.
- Others: there are other sectors such as Health, Industry o Transportationamong others, which also apply Data Governance to ensure quality, security, traceability and regulatory compliance in the management of critical information.
Relationship between Data Governance and other disciplines
The Data Governance does not act alone. It is directly related to other key disciplines such as:
- Data Qualityto ensure the veracity of the information.
- Data StewardshipActive data management in your day-to-day business.
- Big Data and Data Analyticsensures that large volumes of data are organized and ready for analysis.
There are also international standards that support this discipline, such as the DAMA-DMBOK, standards ISO/IEC 38505 or guides of the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology).





